Dr. V.K.Maheshwari, M.A. (Socio, Phil) B.Sc. M. Ed, Ph.D. Former Principal, K.L.D.A.V.(P.G) College, Roorkee, India
Mrs Sudha Rani Maheshwari, M.Sc (Zoology), B.Ed. Former Principal. A.K.P.I.College, Roorkee, India
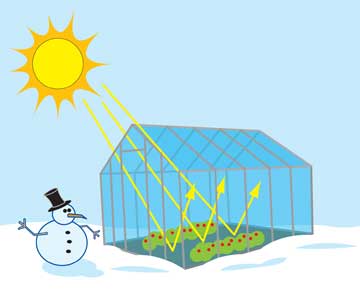 The green house means a building made mainly of glass, with heat and humidity regulated for growing plants. The atmosphere acts like a glass in green house. In a green house, visible light passes through the glass and heats up the soil warming the plants. The warm soil emits radiation in longer wave-length-opaque to longer wave length of infra-red radiation; it partly reflects and partly absorbs infra-red radiations. This mechanism keeps the green house warmer than the outer atmosphere.
The green house means a building made mainly of glass, with heat and humidity regulated for growing plants. The atmosphere acts like a glass in green house. In a green house, visible light passes through the glass and heats up the soil warming the plants. The warm soil emits radiation in longer wave-length-opaque to longer wave length of infra-red radiation; it partly reflects and partly absorbs infra-red radiations. This mechanism keeps the green house warmer than the outer atmosphere.
In a similar way, the earth’s atmosphere battles up the energy of the sun, and is said to act like a green house, where Carbon dioxide acts like glass windows. Carbon dioxide and water vapors in the atmosphere transmit short wavelength solar radiations but reflect the longer wavelength heat radiation from warmed surface of the earth molecules Carbon dioxide are transparent to sunlight but not to the heat radiation. So they trap and re-enforce the solar heat stimulating an effect which is known as green house effect.
The greenhouse effect is the phenomenon whereby the earth’s atmosphere traps solar radiation, caused by the presence in the atmosphere of gases allow incoming sunlight to pass through but absorb heat radiated back from the earth’s surface. Atmospheric heating caused by solar radiation being readily transmitted inward through the earth’s atmosphere but long wave radiation less readily transmitted outward, due to absorption by certain gases in the atmosphere.
The science surrounding this phenomenon first appeared in print in the 1820s. Since then researchers have added countless refinements to the complexity of the discovery. The greenhouse effect was discovered and published in 1824 by the French mathematician Jean-Baptiste-Joseph Fourier (1768-1830).The greenhouse effect was first studied in 1896 by the Swedish Nobel-laureate (1903). Chemist Svante Arrhenius (1859-1927) who called it hothouse effect
Since there is considerable misunderstanding and misconceptions regarding the greenhouse effect, it is useful to list a few of the things the greenhouse effect is not:
1) Greenhouse effect does not operate like a greenhouse that plants are grown in. Plant greenhouses stay warm because they are enclosed, preventing warm air from escaping. In the open atmosphere, warm air that builds up at the surface rises (“converts”) and mixes with air from higher altitudes, limiting warming near the surface. The atmospheric greenhouse effect is radioactive, not convective.
2) The greenhouse effect does not require solar radiation (sunlight) to operate. The greenhouse effect would still exist if there was no sun, and the climate system was instead warmed from below by geothermal energy.
3) The greenhouse effect cannot be demonstrated with a jar or other enclosure because there is too little greenhouse gas involved. Thousands of feet of atmospheric depth are required for the greenhouse effect to have a measurable effect on temperature.
The greenhouse effect is entirely due to the fact that the atmosphere absorbs and emits infrared energy, combined with a heat source to warm the bottom of the atmosphere (in our case, the Sun) and the cold depths of outer space above the top of the atmosphere. The greenhouse gases (and clouds) reduce the ability of the Earth’s surface to cool, thus raising its temperature above what it would be without those greenhouse gases.
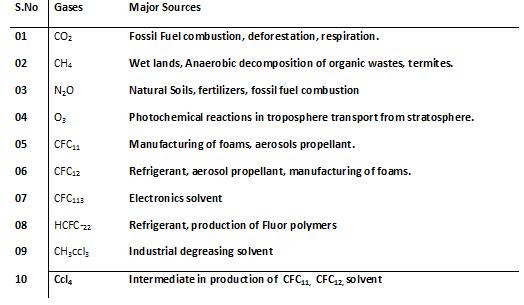
Major Sources of Green house Gasses
There are two common meanings of the term “greenhouse effect”. There is a “natural” greenhouse effect that keeps the Earth’s climate warm and habitable. There is also the “man-made” greenhouse effect, which is the enhancement of Earth’s natural greenhouse effect by the addition of greenhouse gases from the burning of fossil fuels (mainly petroleum, coal, and natural gas).
The strength of the Earth’s greenhouse effect is determined by the concentration in the atmosphere of a handful of greenhouse gases. The one that causes the most warming overall is water vapors – though human activity affects its level in the atmosphere indirectly rather than directly.
‘Greenhouse gases’ is a term used to describe naturally-occurring and human-manufactured gases that trap heat in the atmosphere. These greenhouse gases are water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxides, and chlorofluorocarbons or CFCs). . Although, these gases form only around 1% of our atmosphere, they are extremely vital in maintaining the ecological balance and sustaining life on this planet. Without the presence of these gases, the temperature of the earth would have been lesser than 30°C, which means that survival of living species wouldn’t be possible. The greenhouse effect can be thought of a process through which nature maintains a balance in the atmosphere.
Greenhouse gases, move in and out of the atmosphere. They trap some of the heat radiated out from the Earth that would normally move out into space. This is called the greenhouse effect. It is natural, and is caused by the earth’s carbon and water cycles and the heat from the sun. Without this warming we would be a cold dead planet.
Process of Greenhouse Effect
The Green House effect may therefore be explained as the progressive warming up of the earth’s surface due to blanketing effect of manmade Carbon dioxide in the atmosphere.
The greenhouse effect refers to circumstances where the short wavelengths ofvisible light from the sun pass through a transparent medium and are absorbed, but the longer wavelengths of the infrared re-radiation from the heated objects are unable to pass through that medium. The trapping of the long wavelength radiation leads to more heating and a higher resultant temperature. Besides the heating of an automobile by sunlight through the windshield and the namesake example of heating the greenhouse by sunlight passing through sealed, transparent windows, the greenhouse effect has been widely used to describe the trapping of excess heat by the rising concentration of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. The carbon dioxide strongly absorbs infrared and does not allow as much of it to escape into space.
Steady increase in the Earth’s average lower atmosphere (near surface) temperature due to heat retention caused by the accumulation of greenhouse gases These gases form a blanket around the earth that lets the incoming sun rays (short wave radiation) to pass through but blocks the reflected heat rays (long wave radiation) from going out into the space. Heat-retention is a natural phenomenon (essential to all life on earth) replicated in greenhouses where the glass roof traps radiant heat within an enclosed space.
Sunlight is one of the major sources of energy for living organisms. Apart from helping us with various energy needs, it also helps in keeping the atmosphere warm. When sunrays strike the surface of the earth, they are partly absorbed, and partly reflected back into the atmosphere. These reflected rays, known as infrared radiations, are captured by ‘greenhouse gases’, which helps in keeping our atmosphere warm.
The greenhouse gasses present in the atmosphere are also capable of absorbing long wave radiation and radiate energy back to the earth. When these gases increase in the atmosphere as a result of air pollution or human activities more energy is radiated back and consequently temperature of the earth increases. This phenomenon is known as green house effect or global warming.
Greenhouse Effect: Causes
Causes of this natural greenhouse effect:
The way the planet Earth is heated and cooled is, the Earth is heated by visible light from the sun during the day, and it cools off at night by radiating infra-red radiation to space. The earth’s water and carbon cycles move water vapors and carbon dioxide in and out of the atmosphere constantly. These gases are known as greenhouse gases, and have the property of being transparent to visible light but opaque to infra-red light. They absorb the infra-red radiation coming up from the warm earth and prevent some of it escaping to space. The warmed greenhouse gases then re-radiate heat, some of which goes back to earth. So they allow heat in during the day but prevent it from escaping at night.
Effects of this natural greenhouse effect
The earth is comfortably warm enough for life. Without this greenhouse effect human life on earth would be impossible as the earth would be in a permanent Ice Age. If too much of the Antarctic glaciers melt, sea levels will rise and coastal areas will flood. Agriculture will be disrupted. All weather patterns will change, with increased floods and increased droughts in various locations. There will be very big problems. The long-term natural greenhouse effect that has kept the earth warm for millions of years
Causes that enhance greenhouse effect
The second greenhouse effect is known as the enhanced, or accelerated greenhouse effect. Extra carbon dioxide (CO2) has been added to the atmosphere by human activity, largely since the beginning of the Industrial Age,
Deforestation
One of the major reasons for the greenhouse effect is deforestation. With the increase in population, more and more forests are being cut to provide accommodation and other amenities to people. Thus one of the man-made causes of the greenhouse effect is deforestation. Deforestation increases the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. Also, due to the disappearance of trees, photosynthesis cannot take place. Deforestation is rampant today due to the burden of our needs on land. . Trees use carbon dioxide and give off oxygen in its place, which helps to create the optimal balance of gases in the atmosphere. The levels of deforestation have increased by about 9% in recent times..
Burning of Fossil Fuels
We all know that burning of fossil fuels, like petroleum and oil, wood and gas results in release of pollutants into the atmosphere. Greenhouse gases can also be released into the atmosphere due to the burning of fossil fuels, oil, coal and gas. These materials are used increasingly and rampantly in industries. Most factories also produce many gases which last for a longer time in the atmosphere. These gases contribute to the greenhouse effect and also increase the global warming on the planet. These gases are not naturally available in the atmosphere. Therefore industries are also a major cause of the greenhouse effect.
Electrical Appliances
Other man-made cause of the increase in the greenhouse effect is the emission of greenhouse gases by electrical appliances. Electrical appliances are amongst the major contributors to the green house effect. Even the humble refrigerator in the house emits gases which contribute to the greenhouse effect. These gases are known as Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) and are used in refrigerators, aerosol cans, some foaming agents in the packaging industry, fire extinguisher chemicals, and cleaners used in the electronic industry. Some processes of the cement manufacturing industries also act as a cause towards the greenhouse effect.
Population Growth
Population growth is an indirect contributor and one of the major causes of the greenhouse effect. With the increase in population, the needs and wants of people increase. This increases the manufacturing and the industry process. This results in the increase of the release of industrial gases which catalyze the greenhouse effect.
Impact of Green house
These were some factors that cause an increase in the greenhouse effect. As mentioned before, it is not the greenhouse effect that causes global warming; it is the unrestrained human activity that has caused an increase in the greenhouse gases, which in turn have led to global warming. The need of the hour is to spare a thought on the damage that we might be causing to the environment. We may not live long enough to witness the repercussions of our actions, but our future generations might have to pay for our actions
Global warming is causing climate change. This increase in the temperature of the Earth has many effects. We are presently seeing the melting of a lot of glaciers, increased amounts of flooding in many areas, and increasingly violent weather, with more powerful hurricanes on average than we used to have. Winters may become shorter, but harsher. Summers may become increasingly hotter. Hurricanes and tornadoes may become gradually stronger and more common, and their range may become larger.
This may have a dramatic affect on many different animals, especially those that thrive and require very cold, or very hot climates. So far the effects are minor. Much more serious effects will result if this trend continues. Few clearly visible impacts are :
Increase in the global temperature- Today, the increase in the Earth’s temperature is increasing with unprecedented speed. To understand just how quickly global warming is accelerating, consider this: During the entire 20th century, the average global temperature increased by about 0.6 degrees Celsius (slightly more than 1 degree Fahrenheit).
Using computer climate models, scientists estimate that by the year 2100 the average global temperature will increase by 1.4 degrees to 5.8 degrees Celsius (approximately 2.5 degrees to 10.5 degrees Fahrenheit). Scientists agree that even a small increase in the global temperature would lead to significant climate and weather changes, affecting cloud cover, precipitation, wind patterns, the frequency and severity of storms, and the duration of seasons.
- Rising temperatures would raise sea levels as well, reducing supplies of fresh water as flooding occurs along coastlines worldwide and salt water reaches inland.
- Many of the world’s endangered species would become extinct as rising temperatures changed their habitat.
- Millions of people also would be affected, especially poor people who live in precarious locations or depend on the land for a subsistence living.
- Certain vector-borne diseases carried by animals or insects, such as malaria, would become more widespread as warmer conditions expanded their range.
Carbon Dioxide Emissions are the Biggest Problem- Currently, carbon dioxide accounts for more than 60 percent of the enhanced greenhouse effect caused by the increase of greenhouse gases, and the level of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere is increasing by more than 10 percent every 20 years. If emissions of carbon dioxide continue to grow at current rates, then the level of the gas in the atmosphere will likely double, or possibly even triple, from pre-industrial levels during the 21st century.
Climate Changes are Inevitable- According to the United Nations, some climate change is already inevitable because of emissions that have occurred since the dawn of the Industrial Age.
While the Earth’s climate does not respond quickly to external changes, many scientists believe that global warming already has significant momentum due to 150 years of industrialization in many countries around the world. As a result, global warming will continue to affect life on Earth for hundreds of years, even if greenhouse gas emissions are reduced and the increase in atmospheric levels halted.
Rise in Sea Level -Water expands slightly when heated. This explains why global sea levels would rise if the oceans warmed, just as the fluid in a thermometer rises when heated. Since 1900 the world’s average sea level has raised 10-20 cms (4-8 inches) and appears to be rising about 2.5 cms (inch) per decade. About 1/3 of the World’s population and more than a 3rd of the world’s economic infrastructure are concentrated in coastal regions. Current models indicate than an increase in the average atmospheric temperature of 30c would raise the average global sea level by 0.2 – 1.5 meters over the next 50-100 years.
One meter rise would flood low lying areas of major cities such as Shanghai, Cairo, Bangkok, Sydney, Mumbai etc as well as agriculture lowlands and deltas on Egypt, Bangladesh, India and China where much of the World’s rice is grown.
Decrease in food Production – Water is a limiting factor in the growth of many crops, especially in drier areas. Two climate models project that, with warming from a doubling of Co2 over 1988 levels, droughts would occur every other year across much of the world thus having the potential to lower crop yields.
Deterioration in Human Health – A warmer world affect human health by disrupting suppliers of food and fresh water. Sea level rise could spread infections disease by flooding sewage and sanitation systems. The dislocation and possible extinction of certain biological species and ecosystems cannot be ruled out.
Other effects include more evaporate-transpiration in tropic, alternation in existing precipitation patterns, effect on hydrological cycle etc.
How to Prevent a Green House Effect
- ² Shift over the next 30 years to perpetual and renewable energy resources that don’t emit CO2 .
- ² Ban all, production and uses of CFCs and other Ozone depleting chemicals.
- ² Use energy more efficiently.
- ² Transfer energy efficiency, renewable energy, pollution prevention and waste reduction technologies to LDCs.
- ² Increase the use of nuclear power to produce electricity. This is an option only if safer and cheaper reaction can be developed and if the problem of how to store nuclear waste safely for thousands of years can be solved.
- ² Capture methane gas emitted by landfills and use it as fuel.
- ² Cut beef production to reduce fossil fuel inputs into agriculture.
- ² Reduce carbon dioxide emissions. Walk, take public transportation or ride your bike instead of driving. Carpool with others whenever possible if you must travel by car. Buy locally grown or produced foods; doing so decreases energy use associated with transportation of these products
- ² Conserve electricity by switching off the TV, computer, radio and lights whenever possible. Unplug electronics from the socket when you are not using them. Use compact fluorescent light (CFL) bulbs, which can reduce energy consumption by approximately 60 percent, in place of incandescent light bulbs. Opt for energy-efficient appliances when shopping
- ² Plant trees; they contribute to the absorption of excess carbon dioxide. Providing shade and windbreaks, trees also contribute to creating even temperatures for buildings, thereby reducing the energy requirement for heating or cooling
- ² Keep in mind that heating water requires energy. Reduce your consumption of hot water by washing clothes in cold or warm water. Wait until the dishwasher is full to run it and activate the energy-saving feature if available on your machine. Invest in a low-flow showerhead, which has a lower water flow rate than normal showerheads. Dry your clothes, whenever possible, on a clothesline as opposed to using a mechanical dryer
- ² Reduce nitrous oxide emissions, the majority of which result from agricultural practices. Choose slow-release, low nitrous oxide-emitting fertilizers
- ² Conserve raw materials and energy by recycling or reusing items. Examples include recycling aluminum soda cans and donating or selling old clothing to second-hand stores
- ² Support international global warming legislation. Examples include the Montreal Protocol, which seeks to eliminate the production of CFCs, and the Kyoto Protocol, which aims to limit emissions of the other greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide and methane.